LiDAR Survey
LiDAR which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a method for determining ranges (variable distance) by targeting an object with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. Lidar can also be used to make digital 3-D representations of areas on the earth’s surface, due to differences in laser return times, and by varying laser wavelengths. It has terrestrial, airborne, and mobile applications.

Lidar, is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) to the Earth. These light puls-es—combined with other data recorded by the airborne system — generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics.
Lidar is commonly used to make high-resolution maps, with applications in surveying, geodesy, geomatics, archaeology, geography, forestry, etc.
How it work
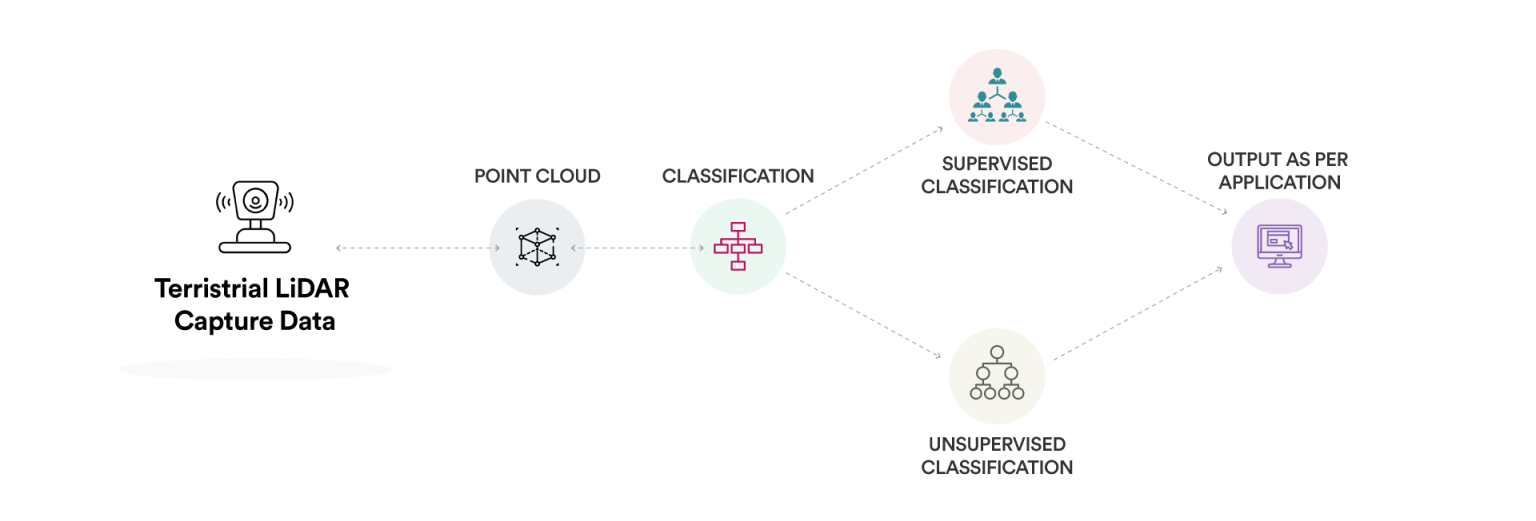
Lidar SURVEY
UAV Generated Data
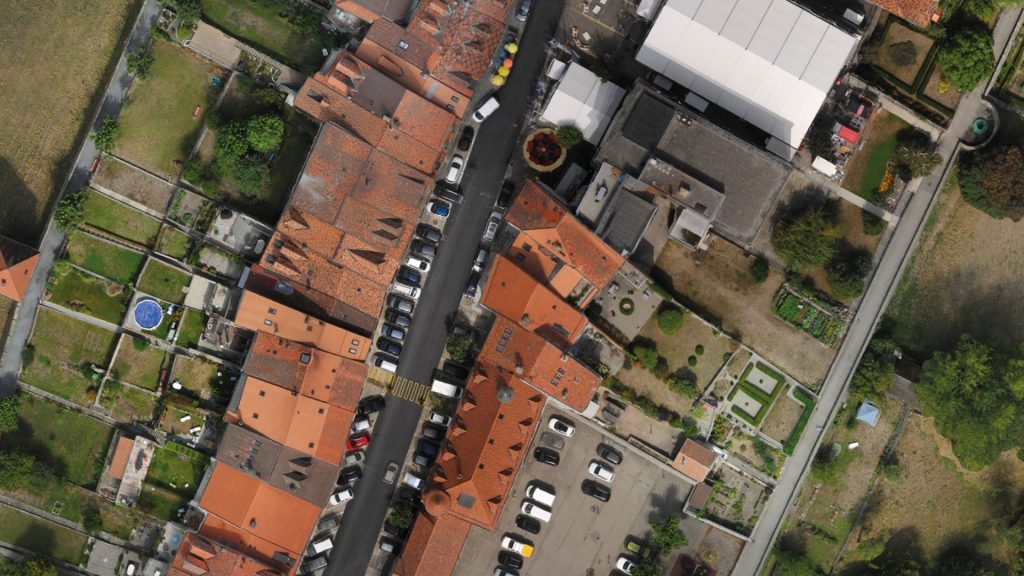

ORTHOMOSAIC
An orthophoto, orthophotograph or orthoimage is an aerial photograph ge-ometrically corrected (“orthorectified”) such that the scale is uniform: the photo has the same lack of distortion as a map. Unlike an uncorrected aerial photo-graph, an orthophotograph can be used to measure true distances, because it is an accurate representation of the earth’s surface, having been adjusted for topographic relief, lens distortion, and camera tilt.
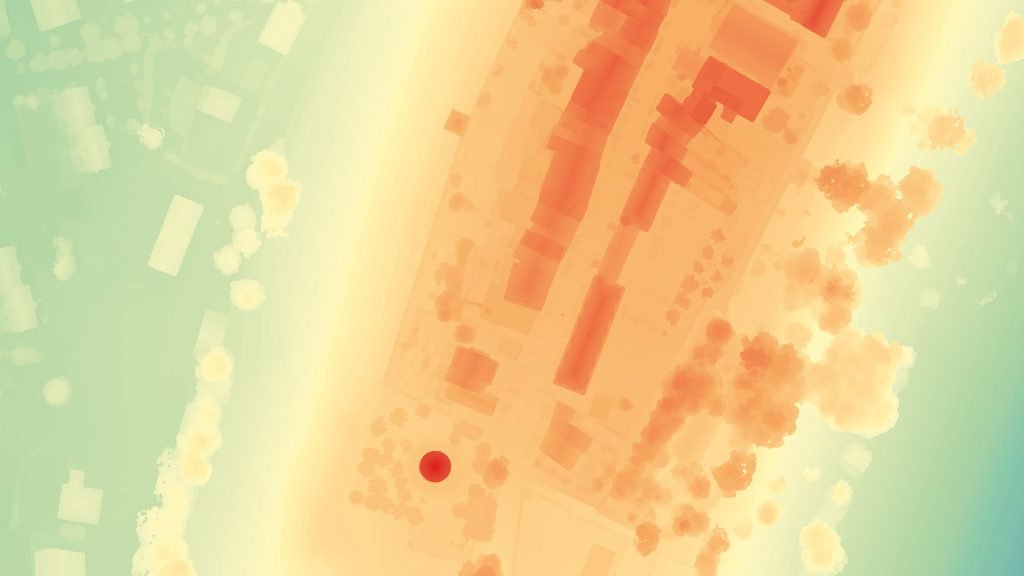

DIGITAL TERRAIN MODEL
Digital Terrain Models (DTM) sometimes called Digital Elevation Models (DEM) is a topographic model of the bare Earth that can be manipulated by computer programs.The data files contain the elevation data of the terrain in a digital for-mat which relates to a rectangular grid. Vegetation, buildings and other cultural features are removed digitally – leaving just the underlying terrain.DTMs are used especially in civil engineering, geodesy & surveying, geophysics, geog-raphy and remote sensing.
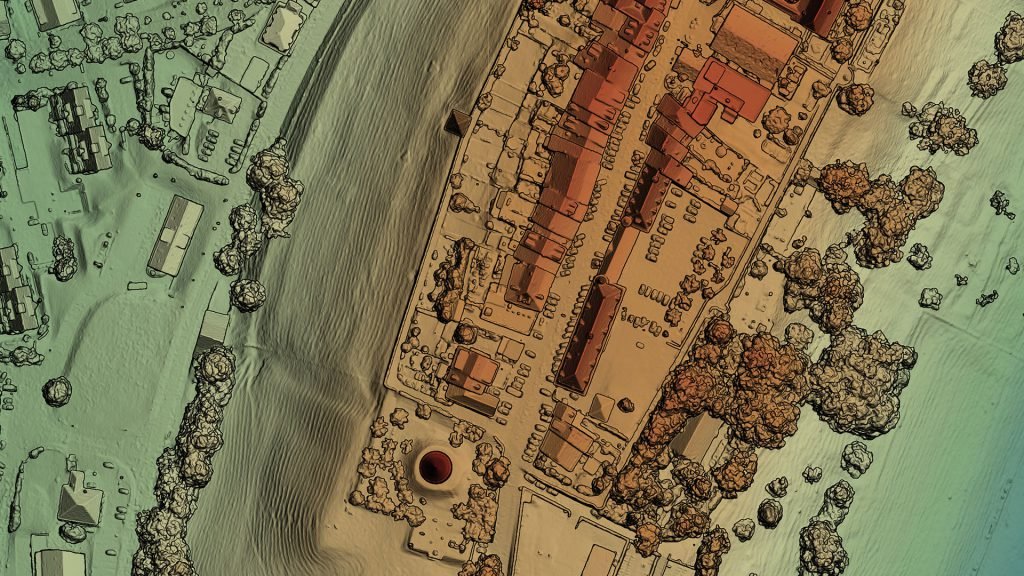

DIGITAL SURFACE MODEL
Digital Surface Model (DSM) that includes ground surface, vegetation and man-made objects. DSM demonstrate the natural and artificial features on the Earth’s surface. Digital Surface Model may be useful for RF planning, land-scape modelling, city modelling, visualization applications and more
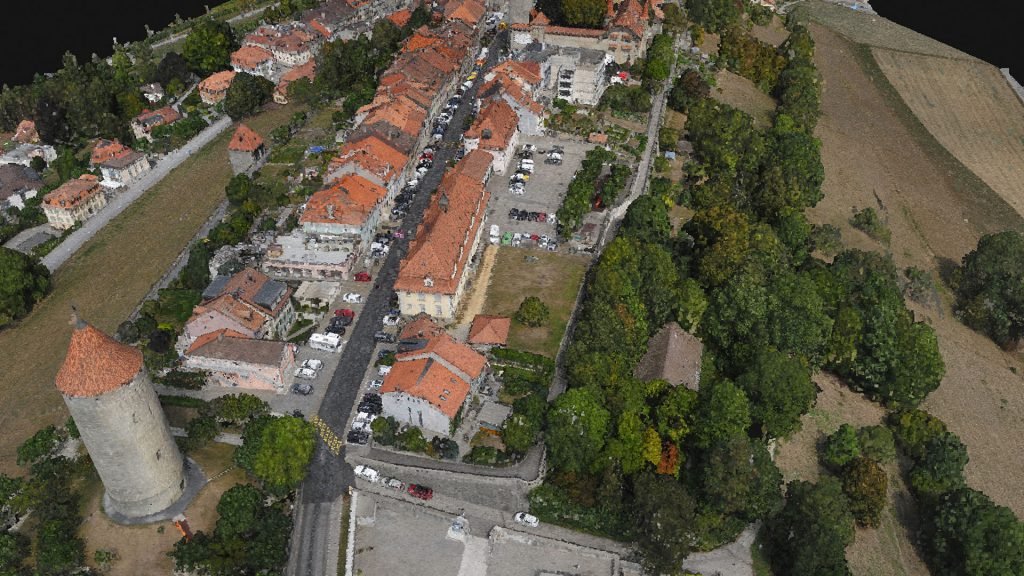

POINT CLOUD
A point cloud is a set of data points in space. The points represent a 3D shape or object. Each point has its set of X, Y and Z coordinates. Point clouds are generally produced by photogrammetry software, which measure many points on the external surfaces of objects around them. As the output of 3D scanning processes, point clouds has many applications.
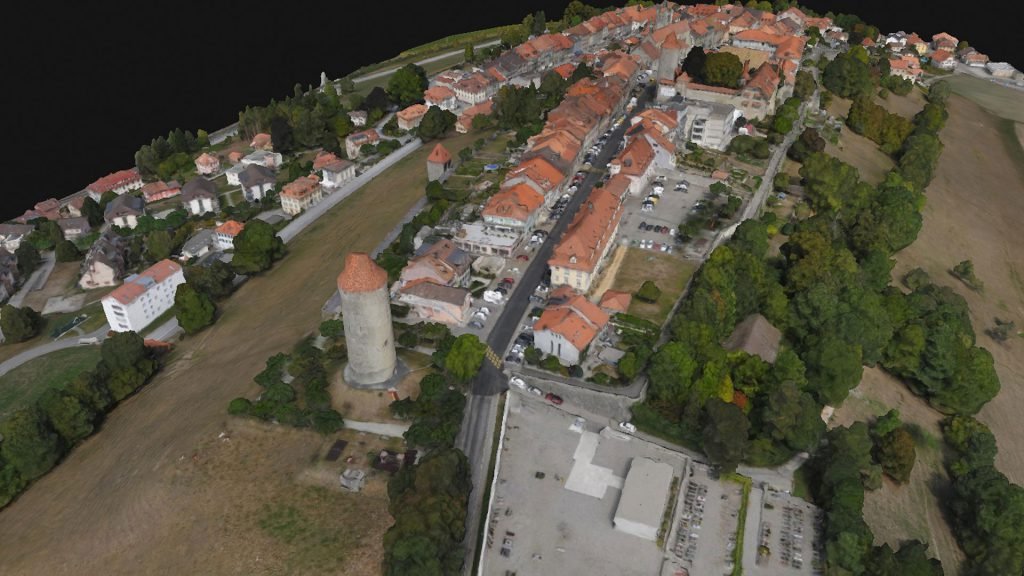

3D MESH
A 3D mesh is the structural build of a 3D model consisting of polygons. 3D meshes use reference points in X, Y and Z axes to define shapes with height, width and depth.
While it can take large numbers of polygons to make a 3D mesh approach photorealism, these relatively simple shapes allow for faster processing than other techniques, like NURBS, that produce smooth curves. The polygons used are typically quadrangles or triangles; these geometric shapes can be further broken down into vertices in X, Y, Z coordinates and lines.
While it can take large numbers of polygons to make a 3D mesh approach photorealism, these relatively simple shapes allow for faster processing than other techniques, like NURBS, that produce smooth curves. The polygons used are typically quadrangles or triangles; these geometric shapes can be further broken down into vertices in X, Y, Z coordinates and lines.
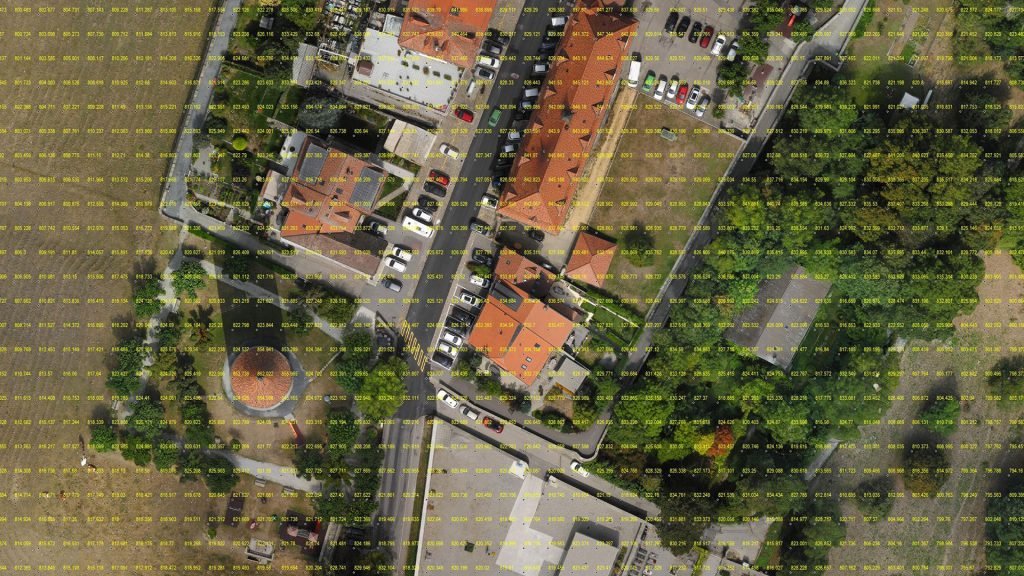

GRID POINTS
The Grid Points are simply the conversion of the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) either DTM or DSM at certain equal intervals. This data is particularly helpful in interoperability between different working software environments.

GEO-TAGGED VIDEOS
Geotagging, or GeoTagging, is the process of adding geographical identifi-cation metadata to various media such as a geotagged photograph or video. Two main options can be used to geotag photos: capturing GPS information at the time the video is taken or “attaching” geocoordinates to the video after the picture is taken.
 LIDAR equipment, which includes a laser scanner, a Global Positioning Sys-tem (GPS), and an Inertial Navigation System (INS), is generally mounted as required on an UAV or ground. The laser scanner transmits brief laser pulses to the ground surface, from which they are reflected or scattered back to the laser scanner. Detecting the returning pulses, the equipment records the time that it took for them to go from the laser scanner to the ground and back. The distance between the laser scanner and the ground is then calculated based on the speed of light.
LIDAR equipment, which includes a laser scanner, a Global Positioning Sys-tem (GPS), and an Inertial Navigation System (INS), is generally mounted as required on an UAV or ground. The laser scanner transmits brief laser pulses to the ground surface, from which they are reflected or scattered back to the laser scanner. Detecting the returning pulses, the equipment records the time that it took for them to go from the laser scanner to the ground and back. The distance between the laser scanner and the ground is then calculated based on the speed of light. Every lidar point can have a classification assigned to it that defines the type of object that has reflected the laser pulse. Lidar points can be classified into a number of categories including bare earth or ground, top of canopy, and water. The different classes are defined using numeric integer codes in the LAS files.
Every lidar point can have a classification assigned to it that defines the type of object that has reflected the laser pulse. Lidar points can be classified into a number of categories including bare earth or ground, top of canopy, and water. The different classes are defined using numeric integer codes in the LAS files.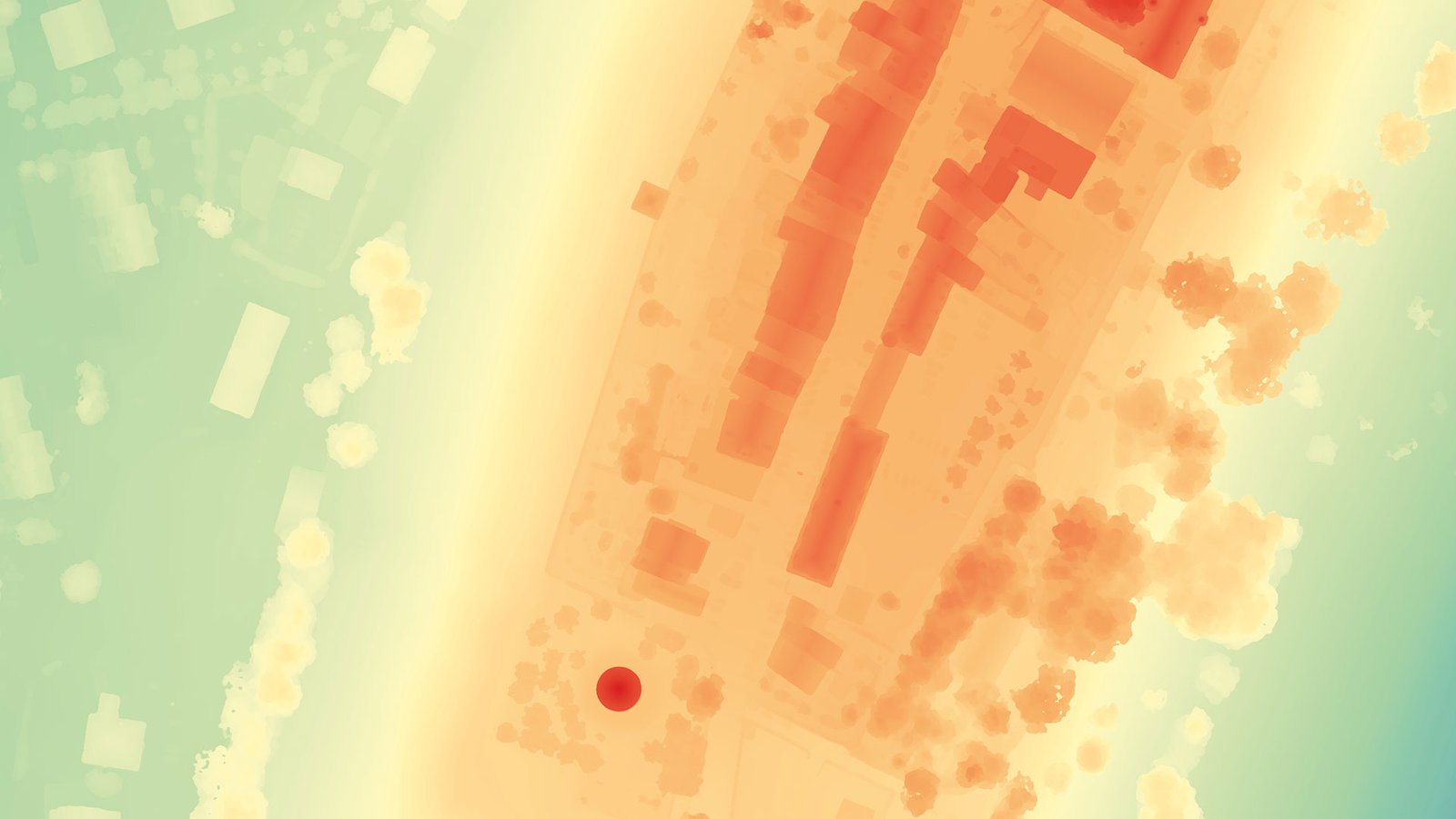 Digital Terrain Models (DTM) sometimes called Digital Elevation Models (DEM) is a topographic model of the bare Earth that can be manipulated by computer programs.The data files contain the elevation data of the terrain in a digital for-mat which relates to a rectangular grid. Vegetation, buildings and other cultural features are removed digitally – leaving just the underlying terrain.DTMs are used especially in civil engineering, geodesy & surveying, geophysics, geog-raphy and remote sensing.
Digital Terrain Models (DTM) sometimes called Digital Elevation Models (DEM) is a topographic model of the bare Earth that can be manipulated by computer programs.The data files contain the elevation data of the terrain in a digital for-mat which relates to a rectangular grid. Vegetation, buildings and other cultural features are removed digitally – leaving just the underlying terrain.DTMs are used especially in civil engineering, geodesy & surveying, geophysics, geog-raphy and remote sensing.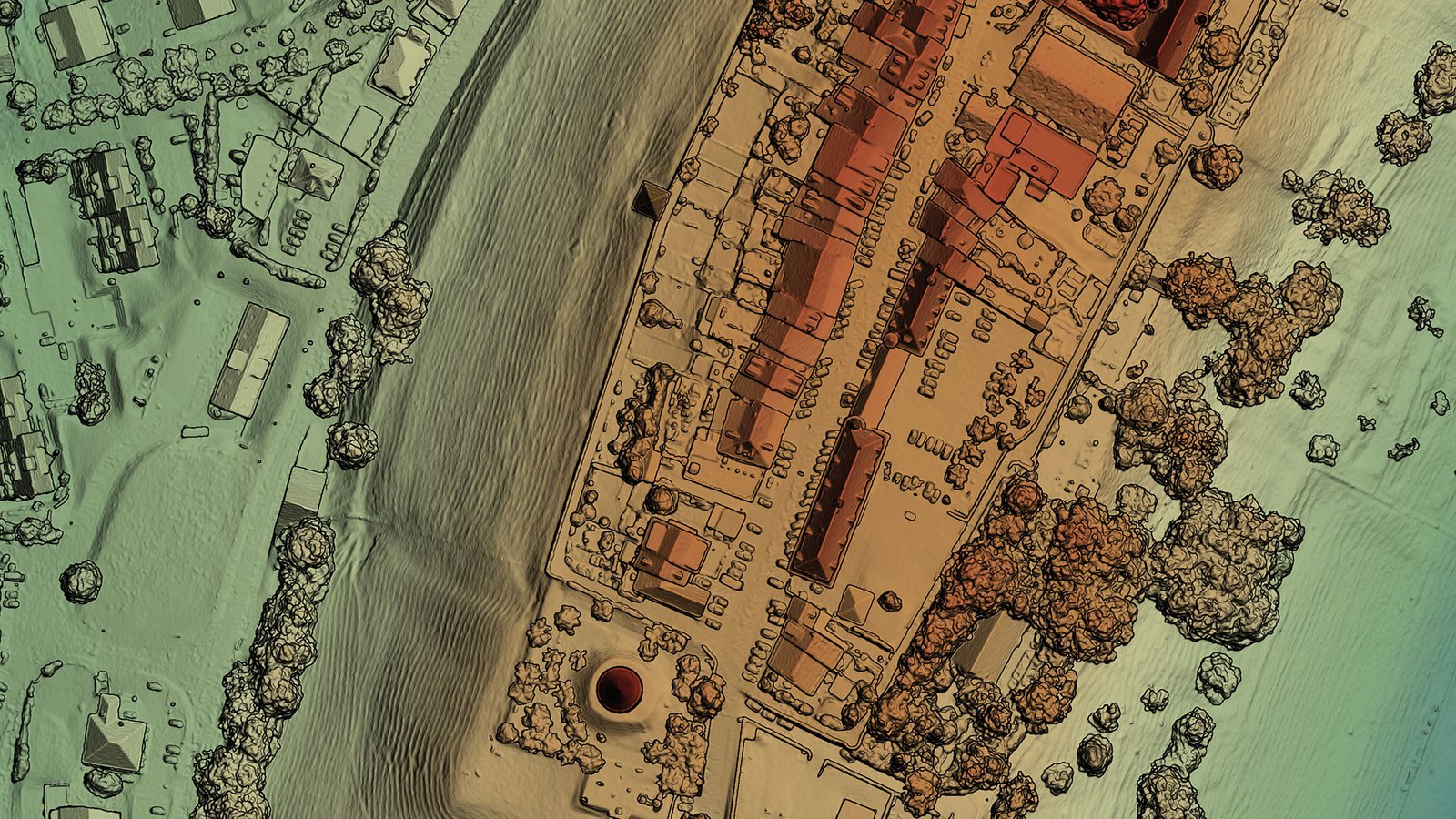 Digital Surface Model (DSM) that includes ground surface, vegetation and man-made objects. DSM demonstrate the natural and artificial features on the Earth’s surface. Digital Surface Model may be useful for RF planning, land-scape modelling, city modelling, visualization applications and more
Digital Surface Model (DSM) that includes ground surface, vegetation and man-made objects. DSM demonstrate the natural and artificial features on the Earth’s surface. Digital Surface Model may be useful for RF planning, land-scape modelling, city modelling, visualization applications and moreLidar SURVEY
Applications of LiDAR
LiDAR data can be burdensome to handle. We at Birds eye provide the complete solution for LiDAR from data capture to classification. Working with LiDAR, one of the archeological surveys we have completed using terrestrial LiDAR. Some other applications of LiDAR in various industries that we deal with are mining for volu-metric analysis, forest mapping, land survey, and data classification.
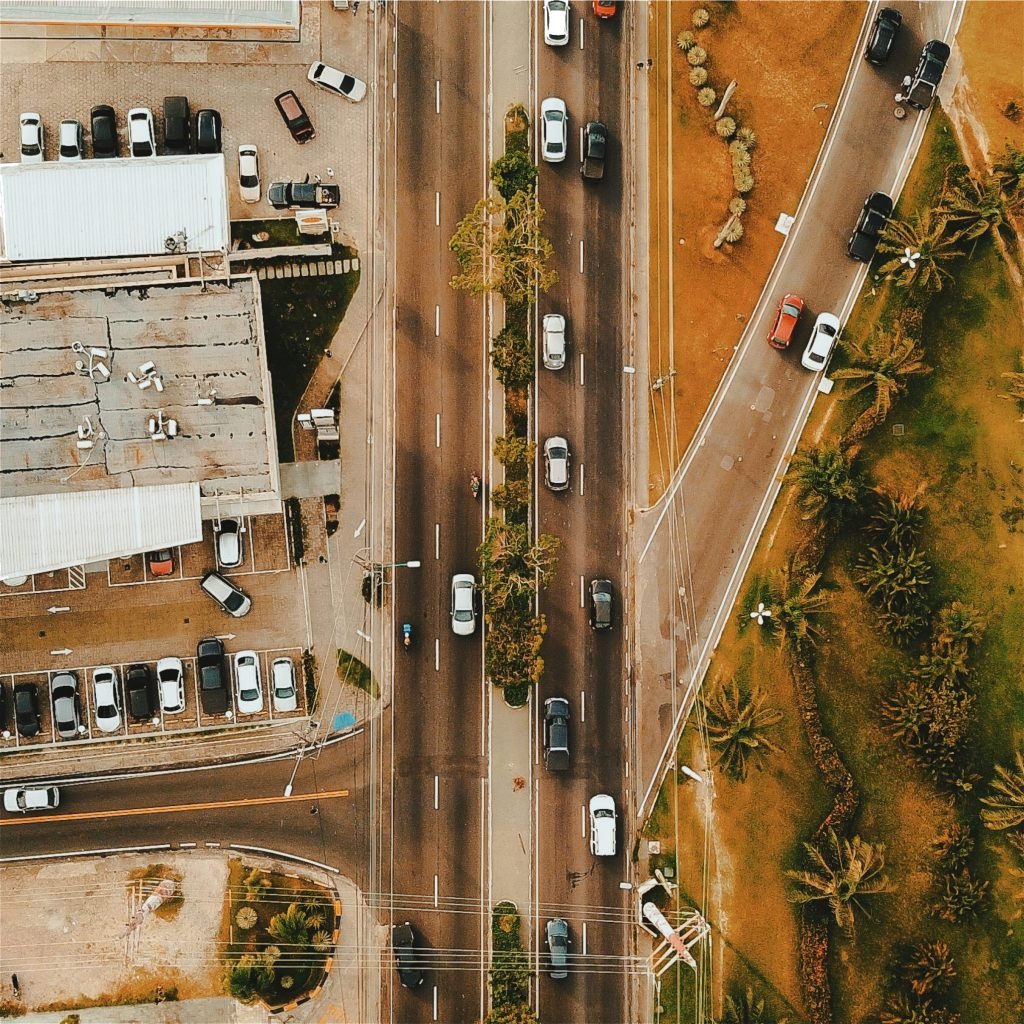

Land Survey
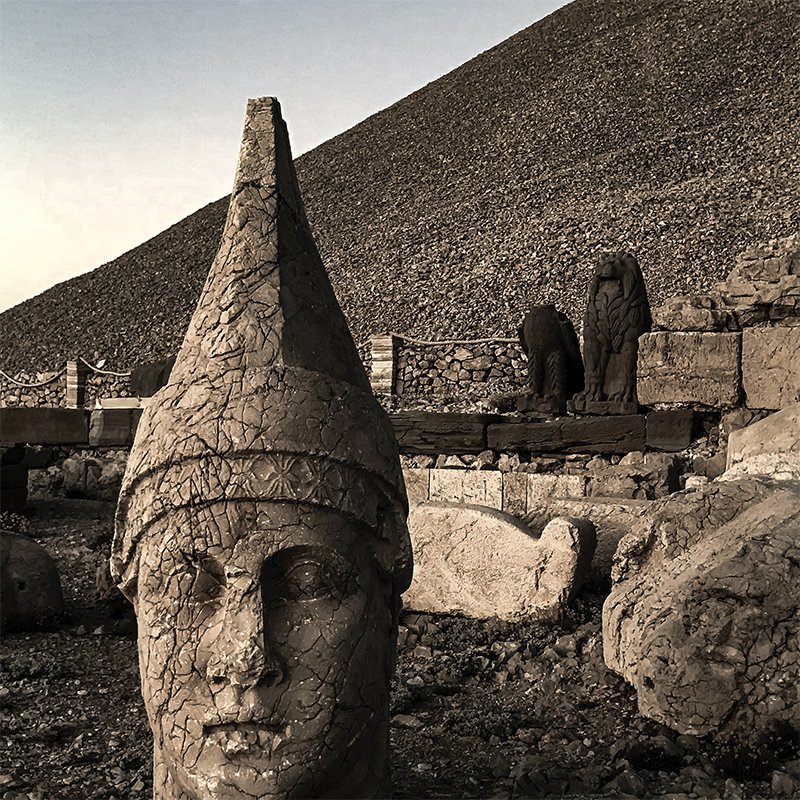

Archiological Survey
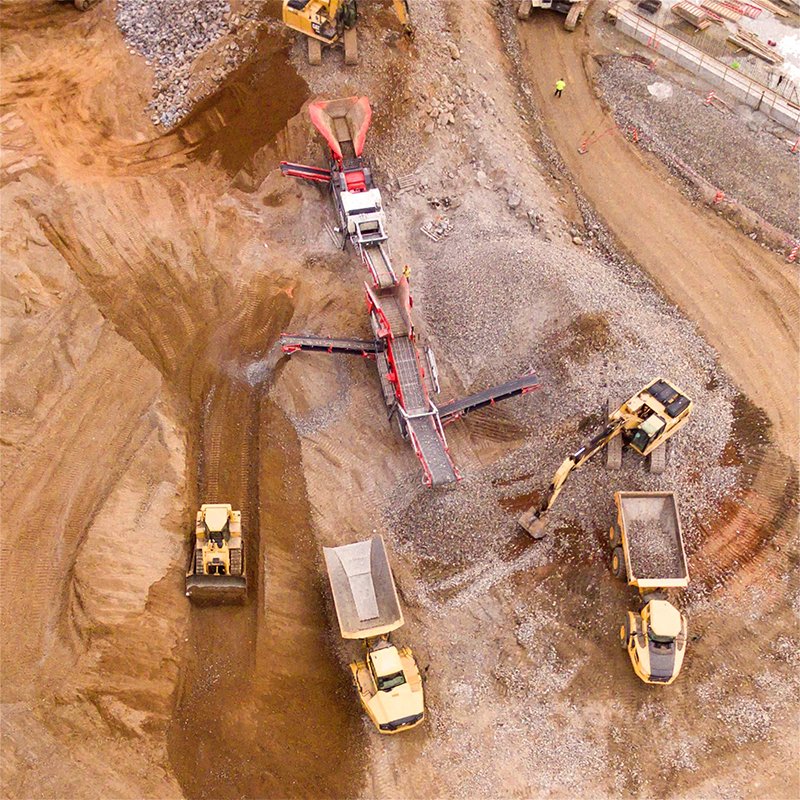

Mining

Data Classification
Let's start something
completely new together
Drop us a line, and we’ll get in touch.
We’ll see if we’re a match and how we can help each other.
We’ll see if we’re a match and how we can help each other.
